
When tackling challenging mechanical or engineering systems, bushings play an essential role in ensuring smooth operation, reducing wear, and prolonging the lifespans of components. If the term leaves you puzzled, don’t worry—we’ll break it down! By the end of this post, you’ll understand what bushings are, what they do, and why they’re essential in so many applications.
Before we go further, be sure to explore detailed information about Steel Bushing and bushings by following our linked resources.
What is the Purpose of a Bushing?
To understand bushings, we must first explore their role in engineering. A bushing definition engineering refers to a cylindrical lining designed to reduce friction and wear between two surfaces in mechanical systems. Acting as a protective interface, bushings serve as support for moving parts, ensuring their motion remains smooth and controlled.
Bushings exert their usefulness across various industries. Whether it’s in automotive suspension, where they minimize vibrations, or heavy machinery, where they reduce shocks, bushings ensure systems operate effectively without unnecessary strain.
They’re also integral in robotics, aerospace, consumer electronics, and renewable energy systems – helping maintain alignment, absorb impact, reduce friction, and prevent metal-on-metal contact that could otherwise lead to mechanical failure, performance loss, or reduced efficiency in high-precision environments. Their compact design and material adaptability make them indispensable even in advanced or space-constrained applications.
For instance, in vehicles an engineering bushing definition typically refers to small, yet sturdy pieces that absorb noise and vibration as the car moves. Over time, they wear out but are easily replaceable, further showcasing their practical utility.
What’s the Difference Between a Bushing and a Bearing?
When discussing bushings, people often question their relationship to or differences from bearings. While there’s some overlap, understanding bushing vs bearing boils down to their specific applications and designs.
- Bushings are simpler components. They’re typically stationary sleeves, often made from robust materials like metal, rubber, or even polymers. Their main job is to reduce friction and isolate vibrations. For example, many machines have bushings installed in areas where motion is rotational or back-and-forth.
- Bearings are more complex. A bushing bearing often includes balls or rollers to allow for free movement with minimal friction. These are commonly used in situations where high-speed rotation is necessary, such as in engines or turbines.
To summarize, bushing vs bearing isn’t an argument about superiority; it’s about fitting the right component into its optimal role. A bush in a suspension system won’t work well in a high-speed motor, just as a complex bearing may be overkill and too costly for low-motion uses.
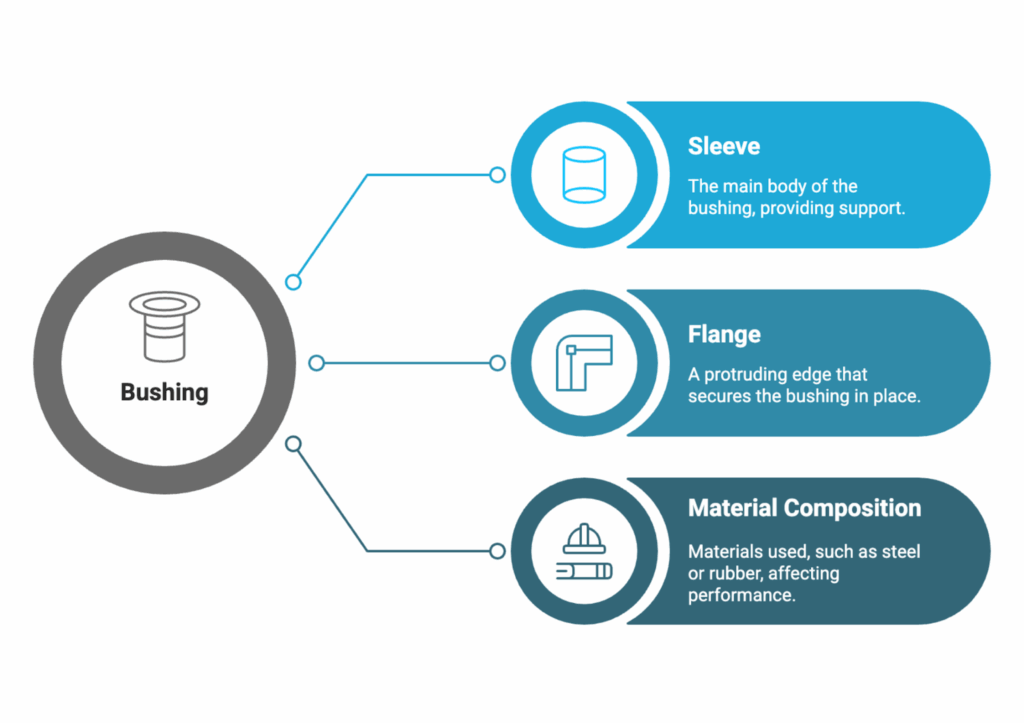
What Does a Bushing Look Like?
Bushings come in several shapes and materials, largely dependent on their function and intended location within a system. The most common forms include cylindrical and flanged bushings. Their outer surface often resembles a smooth sleeve, while the inner surface supports movement. Visually, they may seem unimpressive, but it’s this deceptively simple appearance that makes them so functional in diverse environments.
Steel bushings, rubber bushings, and bonded options are all popular types chosen according to an application’s heat resistance, durability, or flexibility requirements. For example, steel bushings withstand high pressures and temperatures, making them perfect for heavy-duty industrial applications. Alternately, rubber bushings are often utilized in lower-friction systems where absorption of noise and vibration is key.
Can I Drive with Bad Bushings?
Driving with worn-out bushings can lead to problems that may quickly escalate. While you might be able to drive for some time without replacing them, bad bushings present serious risks. Over time, they may compromise your vehicle’s suspension system causing poor handling, uneven tire wear, and increased vibrations.
Any of these signs may indicate your bushings are bad:
- You hear clunking or rattling noises from the vehicle’s suspension.
- The steering feels overly loose.
- There’s visible wear or cracking in the bushing material.
While driving with bad bushings for a short distance might seem manageable, prolonged neglect could result in significant suspension and wheel alignment issues. Address these problems early to prevent costly repairs and ensure a smooth, safe ride.
In Summary
Bushings might be small in size and straightforward in design, but their importance cannot be overstated. From reducing friction to absorbing vibration, these components are the unsung heroes of many industries. Whether you’re dealing with an engineering bushing definition or figuring out the best option between bushing vs bearing, understanding their applications will help you maintain your equipment better.
To learn more about the critical role bushings play or explore detailed specs of Steel Bushing, check out our comprehensive resources. Don’t ignore this critical detail in your equipment. Stay informed, stay efficient, and keep those systems running smoothly.


